Discover 7 doctor-recommended diet changes to lower GGT levels naturally. Learn which foods support liver health, reduce enzyme levels, and promote detox—without medication.
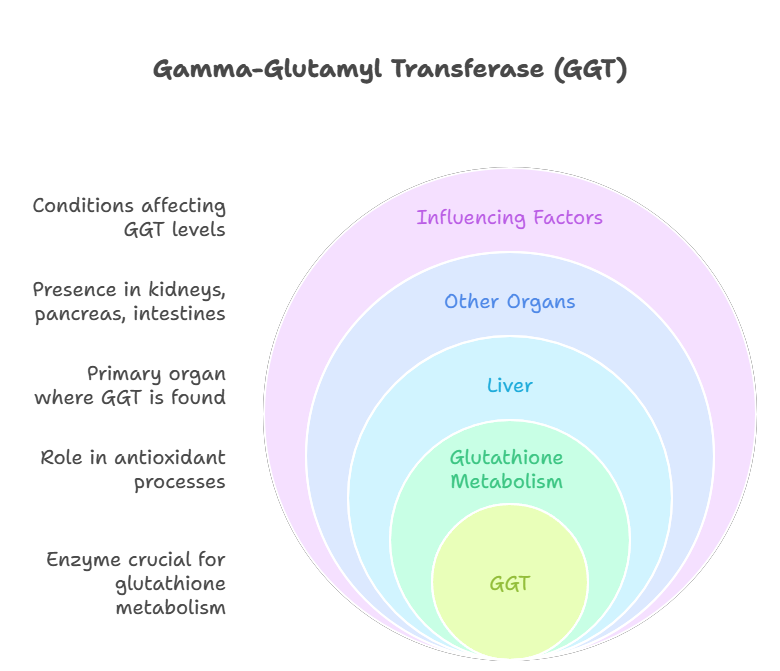
Altered GGT (Gamma-glutamyl transferase) levels, especially if elevated, are often a marker of liver dysfunction, bile duct issues, or alcohol-related liver injury. When GGT is raised in the liver function test (LFT) panel, it suggests oxidative stress or liver inflammation. To support liver health and potentially lower GGT levels, dietary and lifestyle changes can be beneficial.

Have you recently been told your GGT (Gamma-glutamyl transferase) levels are high on a liver function test (LFT)? Don’t panic—this is often a sign that your liver is under stress, not permanent damage. Elevated GGT can result from fatty liver, alcohol intake, obesity, or certain medications.
The good news: Your liver has an amazing ability to heal. By making a few simple but powerful diet changes, you can lower your GGT levels naturally and restore your liver’s vitality.
Let’s explore seven evidence-based, easy-to-follow dietary habits that can make a real difference.
🥦 1. Load Up on Liver-Cleansing Vegetables
Your liver loves antioxidant-rich foods that help it neutralize toxins.
- Eat more cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, and kale.
- Add beetroot, carrots, and spinach to your daily meals—they help reduce liver inflammation.
These vegetables activate natural detox enzymes and can gradually Lower GGT Levels
🍊 2. Add Antioxidant-Rich Fruits for Protection
Fruits rich in vitamin C and polyphenols help protect liver cells from oxidative damage.
Choose:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, blackberries)
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits)
- Papaya and pomegranate
Replace desserts or sweet snacks with 1–2 servings of these fruits each day.
🧄 3. Use Garlic, Turmeric, and Ginger for Natural Detox
These kitchen staples have medicinal properties proven to benefit the liver.
- Garlic helps activate liver enzymes that flush out toxins.
- Turmeric (curcumin) has anti-inflammatory properties that protect liver cells.
- Ginger aids digestion and reduces oxidative stress.
Use them in curries, soups, or teas for daily liver support.
🥑 4. Choose Healthy Fats Over Harmful Ones
The type of fat you eat matters.
- Replace butter and fried oils with olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds.
- Include omega-3-rich fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) twice a week.
These healthy fats lower inflammation and prevent fatty buildup in the liver.
🫛 5. Boost Fiber for Better Detoxification
A fiber-rich diet improves digestion and supports toxin elimination.
Include:
- Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa
- Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and beans
- Fresh fruits and raw vegetables
Aim for at least 25–30 grams of fiber a day to aid liver detox.
🚫 6. Eliminate Alcohol, Processed Foods, and Sugar
Even small amounts of alcohol can raise GGT levels. Avoid:
- Alcohol completely (even “moderate” drinking)
- Processed meats, refined carbs, and deep-fried foods
- Sugary drinks like soda or packaged fruit juices
Your liver needs rest to recover—and these are its biggest stressors.
💧 7. Stay Hydrated for Natural Liver Cleansing
Water helps your liver flush toxins and maintain enzyme balance.
- Drink 8–10 glasses of water daily
- Try lemon water or coconut water for hydration
- Replace sugary drinks with green tea for added antioxidants
🌿 Bonus Tip: Review Medications and Supplements
Some medicines (like painkillers, statins, or anticonvulsants) can affect your GGT levels. Always check with your doctor before stopping or starting any new medicine or supplement.
High GGT levels don’t always mean serious liver disease—they’re often an early warning that your liver needs care. By following these seven diet changes, staying active, and avoiding alcohol, you can lower GGT levels naturally and help your liver heal.
Your body’s best detox system is your liver—so nourish it, protect it, and let it thrive.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is GGT and why does it increase?
GGT (Gamma-glutamyl transferase) is a liver enzyme that helps break down toxins. Levels rise due to alcohol use, fatty liver, medications, or bile duct issues. Learn ways to lower GGT levels.
2. Can diet alone reduce GGT levels?
Yes. For many people, diet and lifestyle changes—especially cutting out alcohol and processed foods—can bring GGT back to normal within a few weeks to months.
3. Which foods are best for reducing GGT?
Foods rich in antioxidants, fiber, and omega-3 fats—like fruits, leafy greens, garlic, and fish—are excellent for liver repair and enzyme balance.
4. How long does it take for GGT levels to improve?
With consistent dietary changes, hydration, and no alcohol, improvement may be seen in 4–8 weeks, depending on the cause.
5. Should I take supplements for liver health?
Some supplements like milk thistle, NAC, and vitamin E may support liver function, but always consult your doctor before using them.
🥦 Dietary Recommendations for Elevated GGT Levels ✅ Recommended Foods High-antioxidant foods (reduce oxidative stress) to lower GGT levels.
Colorful fruits: Berries, oranges, pomegranate, papaya
Vegetables: Spinach, kale, broccoli, beetroot
Green tea
High-fiber foods (support detoxification):
Whole grains (brown rice, oats, quinoa)
Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans)
Raw vegetables and fruits
Liver-supportive foods:
Garlic and onions (contain sulfur, help liver detox)
Turmeric (contains curcumin with anti-inflammatory properties)
Cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage
Good fats (anti-inflammatory):
Omega-3 rich foods: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts
Olive oil (in moderation)
Adequate hydration:
Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins
Coconut water and lemon water are beneficial
🚫 Foods to Avoid: Alcohol – the most important to eliminate, as it directly raises GGT.
Fried and processed foods – increase liver workload and inflammation.
High sugar intake – especially in sodas, sweets, and desserts.
Refined carbohydrates – white bread, pasta, and bakery products.
Red and processed meats – hard on the liver when consumed in excess.
Saturated and trans fats – found in margarine, fast food, packaged snacks.
🛑 Lifestyle Tips Avoid alcohol completely.
Quit smoking – smoking is associated with elevated GGT.
Exercise regularly – helps reduce fat buildup in the liver.
Manage weight – fatty liver is a common cause of raised GGT.
Review medications – some drugs (like phenytoin, NSAIDs, or statins) can affect GGT levels and work against and not lower GGT levels.
✅ Supplements to Discuss with Your Doctor Milk thistle (silymarin) – liver protective
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) – antioxidant and supports glutathione production
Vitamin E & C – antioxidant support (if not contraindicated)
B-complex vitamins – especially B6, B12, and folate
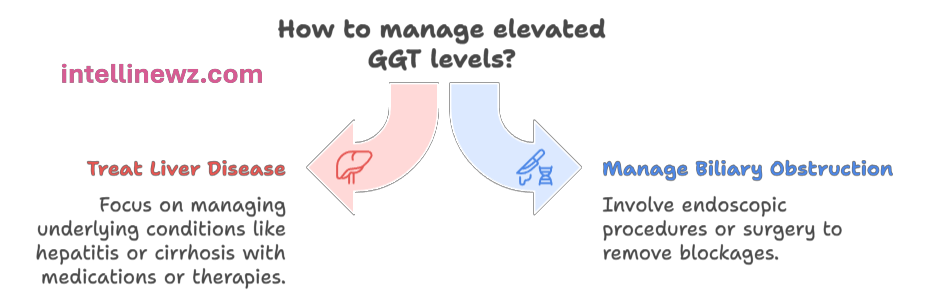
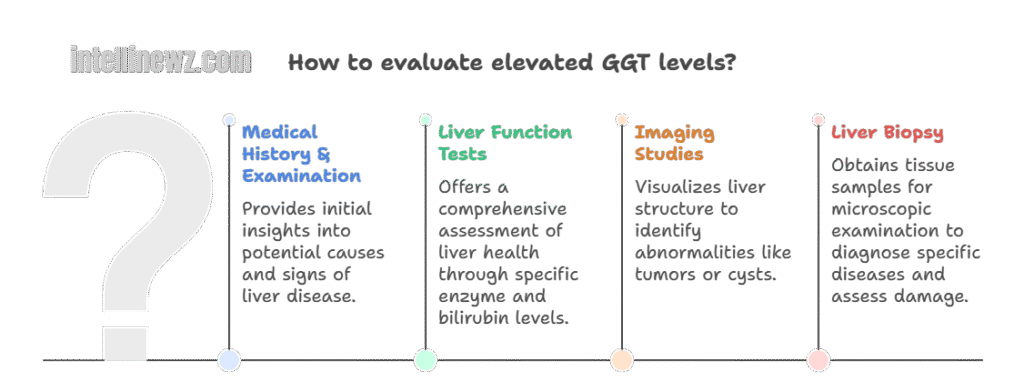
If GGT remains elevated, it’s important to:
Look at other LFT markers (ALT, AST, ALP, bilirubin).
Evaluate for hepatitis, fatty liver, gallbladder issues, or alcohol abuse.
Follow up with imaging or further tests as advised by a healthcare provider.
**************************************************************************************
Disclaimer:
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS
Registered Medical Practitioner (Reg. No. 39739)
With over 30 years of dedicated clinical experience, Dr. Siddiqui has built his career around one clear mission: making quality healthcare affordable, preventive, and accessible.
He is deeply passionate about:
- Early disease diagnosis – empowering patients with timely detection and reducing complications.
- Preventive healthcare – guiding individuals and families towards healthier, longer lives through lifestyle interventions and screenings.
- Affordable treatments – ensuring cost-effective, evidence-based medical solutions that reach people from all walks of life.
Through his blog, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health insights, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust. Every article is rooted in evidence-based medicine and enriched by decades of hands-on clinical practice.
Contact us on: powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not replace personalized medical consultation. For specific health concerns, please consult your physician.
**********This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thanks for supporting the blog!***************************************************************
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS, M.Tech (Biomedical Engineering – VIT, Vellore)
Registered Medical Practitioner – Reg. No. 39739
Physician • Clinical Engineer • Preventive Diagnostics Specialist
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui is a physician–engineer with over 30 years of dedicated clinical and biomedical engineering experience, committed to transforming modern healthcare from late-stage disease treatment to early detection, preventive intelligence, and affordable medical care.
He holds an MBBS degree in Medicine and an M.Tech in Biomedical Engineering from VIT University, Vellore, equipping him with rare dual expertise in clinical medicine, laboratory diagnostics, and medical device engineering. This allows him to translate complex laboratory data into precise, actionable preventive strategies.
Clinical Mission
Dr. Siddiqui’s professional mission centers on three core pillars:
Early Disease Detection
Identifying hidden biomarker abnormalities that signal chronic disease years before symptoms appear — reducing complications, hospitalizations, and long-term disability.
Preventive Healthcare
Guiding individuals and families toward longer, healthier lives through structured screenings, lifestyle intervention frameworks, and predictive diagnostic interpretation.
Affordable Evidence-Based Treatment
Delivering cost-effective, scientifically validated care accessible to people from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
Clinical & Technical Expertise
Across three decades of continuous practice, Dr. Siddiqui has worked extensively with:
Advanced laboratory analyzers and automation platforms
• Cardiac, metabolic, renal, hepatic, endocrine, and inflammatory biomarker systems
• Preventive screening and early organ damage detection frameworks
• Clinical escalation pathways and diagnostic decision-support models
• Medical device validation, calibration, compliance, and patient safety standards
He is recognized for identifying subclinical biomarker shifts that predict cardiovascular disease, diabetes, fatty liver, kidney disease, autoimmune inflammation, neurodegeneration, and accelerated biological aging long before conventional diagnosis.
Role at IntelliNewz
At IntelliNewz, Dr. Siddiqui serves as Founder, Chief Medical Editor, and Lead Clinical Validator. Every article published is:
Evidence-based
• Clinically verified
• Technology-grounded
• Free from commercial bias
• Designed for real-world patient and physician decision-making
Through his writing, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health intelligence, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust — grounded in decades of frontline medical practice.
Contact:
powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content on IntelliNewz is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical consultation. For individual health concerns, please consult your physician.