Os Naviculare Syndrome explained: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for inner foot pain. Learn how this hidden bone affects your arch and mobility.
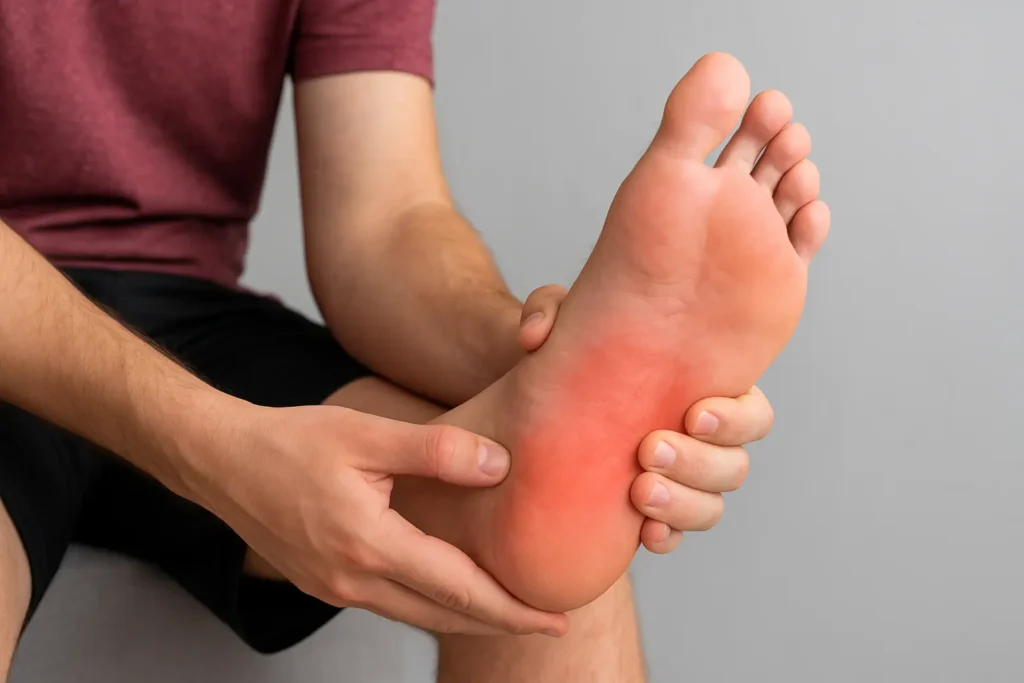
Foot pain on the inner side of the arch can be frustrating, especially when it interferes with walking, sports, or daily activities. One often overlooked cause of this discomfort is Os Naviculare Syndrome, a condition linked to an extra bone in the foot that not everyone knows they have.
Understanding this syndrome is essential for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and long-term foot health.
What Is Os Naviculare Syndrome?
Os Naviculare Syndrome, also known as Accessory Navicular Syndrome, is a painful condition involving an extra bone (or piece of cartilage) located on the inner side of the foot, just above the arch. This extra bone is called the accessory navicular.
While many people with an accessory navicular never experience symptoms, problems arise when this bone becomes irritated or inflamed—leading to Os Naviculare Syndrome.
What Is the Accessory Navicular Bone?
The accessory navicular is a congenital anatomical variant, meaning it is present from birth. It develops alongside the navicular bone, which plays a crucial role in maintaining the foot’s arch and supporting body weight.
There are three main types of accessory navicular bones:
- Type I: Small and round, usually asymptomatic
- Type II: Larger and connected to the navicular by cartilage (most commonly symptomatic)
- Type III: Fused to the navicular, forming an enlarged bone
Type II is most often associated with Os Naviculare Syndrome.
What Causes Os Naviculare Syndrome?
Several factors can trigger symptoms, including:
- Foot trauma or injury
- Overuse from sports or physical activity
- Flat feet or fallen arches
- Ill-fitting footwear that rubs against the bone
- Increased stress on the posterior tibial tendon
The posterior tibial tendon attaches near the navicular bone, and irritation in this area can worsen pain and inflammation.
Common Symptoms of Os Naviculare Syndrome
Symptoms may appear gradually or suddenly, especially after physical strain. Common signs include:
- Pain and tenderness on the inner side of the foot
- Swelling or redness near the arch
- A visible bony prominence
- Pain that worsens with walking, running, or standing
- Difficulty wearing tight or structured shoes
In adolescents, symptoms often appear during periods of rapid growth.
How Is Os Naviculare Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Clinical examination to assess tenderness and foot structure
- X-rays to confirm the presence and type of accessory navicular
- MRI or ultrasound in severe cases to evaluate tendon involvement or inflammation
Early diagnosis helps prevent chronic pain and complications.
Treatment Options for Os Naviculare Syndrome
Non-Surgical (Conservative) Treatments
Most patients improve without surgery. Common approaches include:
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice therapy to reduce inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory medications (as prescribed)
- Supportive footwear
- Custom orthotic inserts
- Physical therapy to strengthen foot muscles
- Temporary immobilization using a walking boot or cast
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered only when conservative treatments fail. The procedure may involve:
- Removal of the accessory navicular bone
- Repair or repositioning of the posterior tibial tendon
Surgical outcomes are generally positive, with most patients returning to normal activity after recovery.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
Os Naviculare Syndrome is more commonly seen in:
- Adolescents and young adults
- Athletes and physically active individuals
- People with flat feet
- Individuals with a family history of foot anomalies
Can Os Naviculare Syndrome Be Prevented?
While the accessory bone itself cannot be prevented, symptoms can often be avoided by:
- Wearing supportive, well-fitted shoes
- Avoiding excessive foot strain
- Using arch supports if you have flat feet
- Addressing foot pain early before it becomes chronic
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent inner foot pain
- Swelling that does not improve with rest
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Pain affecting daily activities or sports performance
Early medical evaluation can prevent long-term complications.
Final Thoughts
Os Naviculare Syndrome is a manageable foot condition that often goes undiagnosed. With proper awareness, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, most individuals can achieve complete pain relief and return to normal activity. If inner foot pain is affecting your quality of life, this condition should not be ignored.
Inner foot pain can be confusing—especially when there’s no obvious injury. Many people assume it’s a sprain, flat feet, or simple overuse. However, for a surprising number of adolescents and adults, the real cause is a little-known condition called Os Naviculare Syndrome.
This condition occurs due to an extra bone on the inner side of the foot that most people don’t even realize they have. While harmless in many cases, this accessory bone can become painful when irritated by walking, sports, tight footwear, or prolonged standing. The result is persistent arch pain that interferes with daily life and mobility.
Because Os Naviculare Syndrome is frequently misdiagnosed or overlooked, many individuals live with discomfort longer than necessary. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step toward lasting relief and healthy foot function.
What is os naviculare syndrome?
Os naviculare syndrome is a painful foot condition caused by irritation of an accessory navicular bone located on the inner side of the foot above the arch.
Is os naviculare syndrome serious?
The condition is not life-threatening, but if left untreated, it can lead to chronic pain, tendon weakness, and difficulty walking or exercising.
Who is most affected by os naviculare syndrome?
It most commonly affects adolescents, athletes, and individuals with flat feet or abnormal foot mechanics.
Can os naviculare syndrome heal without surgery?
Yes. Most cases improve with conservative treatment such as rest, orthotics, physical therapy, and supportive footwear.
What type of shoes are best for os naviculare syndrome?
Supportive shoes with good arch support, cushioning, and a wide inner midfoot area help reduce irritation and pain.
How long does recovery take?
With non-surgical treatment, symptoms often improve within weeks to a few months. Surgical recovery may take several months depending on activity level.
Medical Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational and educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider, orthopedic specialist, or podiatrist regarding foot pain or suspected Os Naviculare Syndrome.
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS, M.Tech (Biomedical Engineering – VIT, Vellore)
Registered Medical Practitioner – Reg. No. 39739
Physician • Clinical Engineer • Preventive Diagnostics Specialist
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui is a physician–engineer with over 30 years of dedicated clinical and biomedical engineering experience, committed to transforming modern healthcare from late-stage disease treatment to early detection, preventive intelligence, and affordable medical care.
He holds an MBBS degree in Medicine and an M.Tech in Biomedical Engineering from VIT University, Vellore, equipping him with rare dual expertise in clinical medicine, laboratory diagnostics, and medical device engineering. This allows him to translate complex laboratory data into precise, actionable preventive strategies.
Clinical Mission
Dr. Siddiqui’s professional mission centers on three core pillars:
Early Disease Detection
Identifying hidden biomarker abnormalities that signal chronic disease years before symptoms appear — reducing complications, hospitalizations, and long-term disability.
Preventive Healthcare
Guiding individuals and families toward longer, healthier lives through structured screenings, lifestyle intervention frameworks, and predictive diagnostic interpretation.
Affordable Evidence-Based Treatment
Delivering cost-effective, scientifically validated care accessible to people from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
Clinical & Technical Expertise
Across three decades of continuous practice, Dr. Siddiqui has worked extensively with:
Advanced laboratory analyzers and automation platforms
• Cardiac, metabolic, renal, hepatic, endocrine, and inflammatory biomarker systems
• Preventive screening and early organ damage detection frameworks
• Clinical escalation pathways and diagnostic decision-support models
• Medical device validation, calibration, compliance, and patient safety standards
He is recognized for identifying subclinical biomarker shifts that predict cardiovascular disease, diabetes, fatty liver, kidney disease, autoimmune inflammation, neurodegeneration, and accelerated biological aging long before conventional diagnosis.
Role at IntelliNewz
At IntelliNewz, Dr. Siddiqui serves as Founder, Chief Medical Editor, and Lead Clinical Validator. Every article published is:
Evidence-based
• Clinically verified
• Technology-grounded
• Free from commercial bias
• Designed for real-world patient and physician decision-making
Through his writing, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health intelligence, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust — grounded in decades of frontline medical practice.
Contact:
powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content on IntelliNewz is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical consultation. For individual health concerns, please consult your physician.



