Breathomics is an emerging field that focuses on the analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) present in exhaled breath. This innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize the early detection of metabolic stress and various health conditions.
By identifying specific VOCs associated with metabolic changes, researchers aim to develop non-invasive diagnostic tools that can provide timely insights into an individual’s health status.
This article explores the principles of breathomics, the significance of VOCs in metabolic stress detection, and the future implications of this technology in clinical practice.
Interactive Breathomics Explorer
🔬 1. What is Breathomics?
Breathomics is the comprehensive analysis of exhaled breath to understand your body’s inner workings. Every time you breathe out, you release hundreds of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—invisible molecules that serve as fingerprints of your cellular health.
Think of it as a window into your metabolism. These VOCs travel from your bloodstream to your lungs, carrying real-time information about what’s happening inside your cells. By analyzing this breathprint, we can detect subtle changes long before symptoms appear.
Key Point: Your breath contains a wealth of medical information — painlessly, instantly, and naturally.
⚙️ 2. How Does It Work?
step ① Sample collection: Breathe normally into a sterile device for 2–5 minutes.
step ② Advanced analysis: Gas chromatography‑mass spectrometry (GC‑MS) identifies individual compounds; electronic nose creates unique “breathprint”.
step ③ AI pattern recognition: Machine learning compares your breathprint to thousands of samples.
Patient experience: Breathe, wait, and receive insights about your metabolic health.
⚠️ 3. Early Detection of Metabolic Stress
Metabolic stress disrupts biochemical balance due to disease, inflammation, or oxidative injury. Breathomics detects these changes at the earliest possible stage — often months before traditional tests show anything.
Real‑world example: In critical illness, elevated aldehydes (propionaldehyde, pentanal) appear as early indicators of oxidative stress and organ dysfunction, allowing rapid intervention.
🎗️ 4. Breast Cancer Detection
Breathomics offers a major breakthrough, especially for women with dense breast tissue. A recent pilot study using a breath analyser demonstrated:
| ✔ Sensitivity | 84% |
| ✔ Specificity | 89% |
The technology detects VOC patterns from altered cancer cell metabolism and lipid peroxidation. A simple, non‑invasive breath test could become a first‑line screening tool.
🫁 5. Metabolic & Gut Health Monitoring
Gut health (SIBO): Measures hydrogen/methane from bacteria to diagnose overgrowth.
Diabetes: Elevated acetone indicates ketosis & blood sugar status.
Insulin resistance: Changing VOC patterns may signal prediabetes.
Portable devices (like OMED Health Analyzer) now enable home monitoring with lab‑comparable accuracy.
📊 6. Advantages Over Traditional Testing
| Traditional | Breathomics |
| Invasive (needles, biopsy) | Completely non‑invasive |
| Single biomarker | Holistic pattern analysis |
| Difficult to repeat | Safe for daily monitoring |
| Results in days | Results in minutes |
Captures dynamic, real‑time metabolism — ideal for monitoring treatment response.
👨⚕️ 7. Message from our Medical Director
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui
“Breathomics transforms breathing into a diagnostic event. It lets us detect disease at the earliest, most treatable stages and tailor treatments to each patient’s unique metabolic profile. This isn’t just a new test — it’s a new way of thinking about health.”
— Medical Director, Cosmo General Hospital
❓ 8. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is the test painful? A: Not at all — you simply breathe into a device.
Q: How do I prepare? A: May require fasting (10‑12h) for gut tests; simpler for cancer screening. Doctor will guide you.
Q: How long does it take? A: Collection 2‑5 min, results in minutes (point‑of‑care) or next day.
Q: Is it covered by insurance? A: Some established tests (SIBO) are covered; newer cancer tests are still research‑stage.
Q: Where can I get tested? A: At Cosmo General specialized clinics — ask your physician.
📋 9. Medical Disclaimer
Important information — Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, Cosmo General Hospital
This information is for general educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Breathomics is an emerging field; many applications are still under investigation and not approved as standalone diagnostic tests.
Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis. Dr. Siddiqui’s commentary reflects his professional perspective but is not a personal consultation.
If you think you have a medical emergency, call emergency services immediately.
Introduction to Breathomics
Breathomics combines the fields of analytical chemistry, biology, and medicine to study the composition of exhaled breath. Human breath contains a complex mixture of gases and VOCs produced as a result of metabolic processes. These compounds can serve as biomarkers for various physiological and pathological conditions.
The non-invasive nature of breath analysis makes it an attractive alternative to traditional diagnostic methods, which often involve blood draws or biopsies.
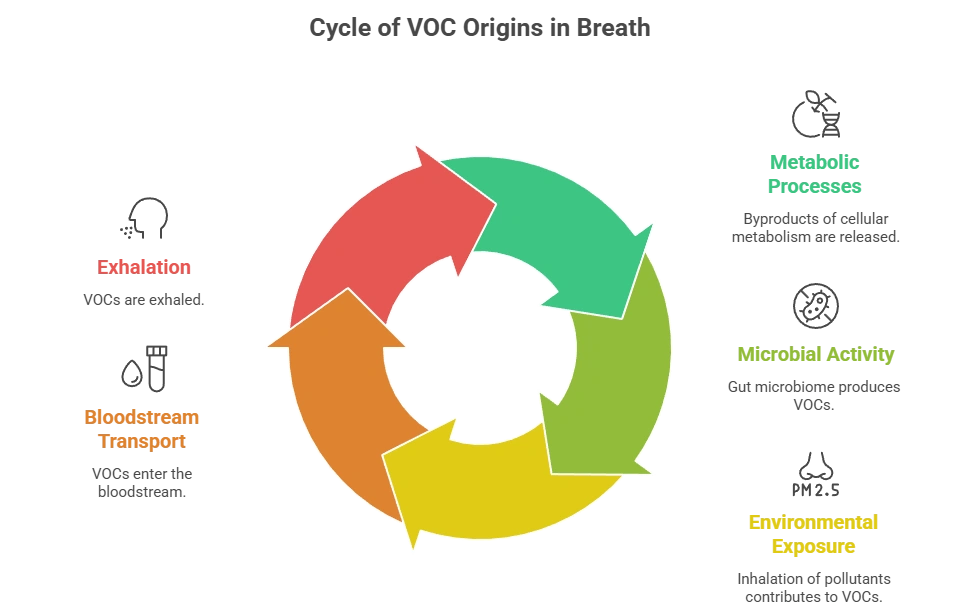
Understanding Volatile Organic Compounds
VOCs are organic chemicals with high vapor pressure at room temperature, allowing them to evaporate easily into the air. In breathomics, VOCs can originate from several sources:
- Metabolic processes: Byproducts of cellular metabolism released into the bloodstream and exhaled.
- Microbial activity: VOCs generated by gut microbiota and other microbial communities.
- Environmental exposure: Inhalation of pollutants or chemicals affecting the VOC profile in breath.

Identifying and quantifying specific VOCs provides valuable information about an individual’s metabolic state and overall health.
Metabolic Stress and Its Implications
Metabolic stress refers to the physiological response of the body to various stressors, including nutritional deficiencies, physical exertion, and environmental factors.
Persistent metabolic stress can contribute to obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome. Early detection is crucial to prevent disease progression and enable timely intervention.
The Role of Breathomics in Detecting Metabolic Stress
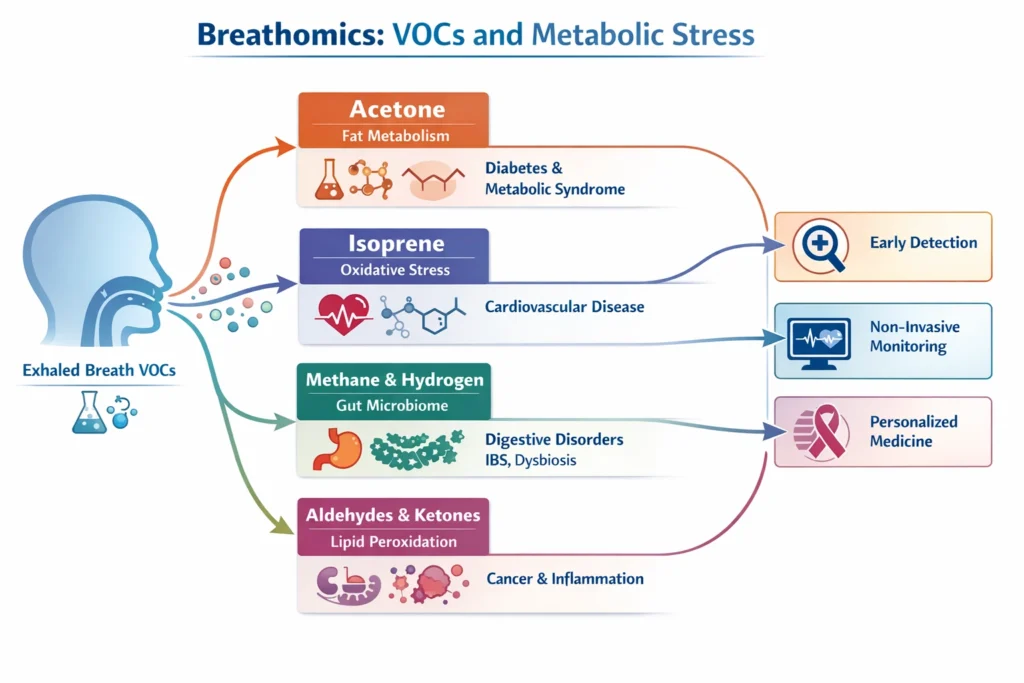
Studies show that specific VOCs in exhaled breath serve as biomarkers for metabolic stress. Elevated levels of aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols often indicate metabolic dysregulation.
By analyzing breath samples under various stress conditions, researchers can identify VOC patterns that correlate with metabolic changes.
Key Biomarkers
- Acetone: Linked to fat metabolism; elevated levels indicate increased lipolysis during metabolic stress.
- Isoprene: Associated with cholesterol synthesis; can reflect stress-induced metabolic changes.
- Ethylene: Marker for oxidative stress, often elevated during metabolic disturbances.
Analytical Techniques
Several analytical techniques are used in breathomics:
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Separates and identifies VOCs with high sensitivity and specificity.
- Electronic Nose Technology: Sensor arrays detect VOC patterns rapidly, offering real-time results.
Challenges and Limitations

Despite its promise, breathomics faces several challenges:
- Standardization: Protocols for breath sample collection and analysis must be standardized for reproducible results.
- Complexity of Breath Composition: The wide variety of VOCs makes pinpointing specific biomarkers challenging.
- Individual Variability: Age, sex, diet, and lifestyle can influence VOC profiles, requiring personalized analysis.
Future Implications

Breathomics holds tremendous potential for clinical practice:
- Portable Devices: Future technology may enable routine metabolic stress screening in clinics, sports medicine, and remote settings.
- Integrated Diagnostics: Combining breathomics with blood tests or imaging can enhance metabolic assessments.
- Personalized Medicine: VOC profiling can guide tailored interventions, diet, and lifestyle strategies.
- Public Health Applications: Early detection of metabolic stress in at-risk populations allows targeted prevention of chronic diseases.
Conclusion
Breathomics offers a groundbreaking, non-invasive approach to understanding metabolic stress through the analysis of exhaled VOCs. By leveraging the unique chemical signatures in breath, clinicians and researchers can gain actionable insights into metabolic health and disease.
As the field advances, breathomics has the potential to transform early detection, monitoring, and personalized management of metabolic disorders, paving the way for innovative healthcare solutions worldwide.
FAQ 1: What is breathomics and how does it work?
Answer:
Breathomics is the study of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath. These VOCs are byproducts of metabolism, microbial activity, or oxidative stress. By analyzing their patterns, researchers can identify early signs of metabolic stress and other health conditions non-invasively.

FAQ 2: Which VOCs indicate metabolic stress in breath analysis?
Answer:
Key VOCs linked to metabolic stress include acetone (fat metabolism), isoprene (cholesterol synthesis), and aldehydes/ketones (oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation). Changes in their levels can signal early metabolic disturbances before symptoms appear.
FAQ 3: How can breathomics improve early disease detection?
Answer:
Breathomics enables non-invasive, real-time monitoring of metabolic health. By detecting subtle VOC changes, clinicians can identify metabolic stress, diabetes risk, cardiovascular issues, and even cancer earlier than traditional tests, allowing timely intervention and personalized treatment.

Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS, M.Tech (Biomedical Engineering – VIT, Vellore)
Registered Medical Practitioner – Reg. No. 39739
Physician • Clinical Engineer • Preventive Diagnostics Specialist
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui is a physician–engineer with over 30 years of dedicated clinical and biomedical engineering experience, committed to transforming modern healthcare from late-stage disease treatment to early detection, preventive intelligence, and affordable medical care.
He holds an MBBS degree in Medicine and an M.Tech in Biomedical Engineering from VIT University, Vellore, equipping him with rare dual expertise in clinical medicine, laboratory diagnostics, and medical device engineering. This allows him to translate complex laboratory data into precise, actionable preventive strategies.
Clinical Mission
Dr. Siddiqui’s professional mission centers on three core pillars:
Early Disease Detection
Identifying hidden biomarker abnormalities that signal chronic disease years before symptoms appear — reducing complications, hospitalizations, and long-term disability.
Preventive Healthcare
Guiding individuals and families toward longer, healthier lives through structured screenings, lifestyle intervention frameworks, and predictive diagnostic interpretation.
Affordable Evidence-Based Treatment
Delivering cost-effective, scientifically validated care accessible to people from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
Clinical & Technical Expertise
Across three decades of continuous practice, Dr. Siddiqui has worked extensively with:
Advanced laboratory analyzers and automation platforms
• Cardiac, metabolic, renal, hepatic, endocrine, and inflammatory biomarker systems
• Preventive screening and early organ damage detection frameworks
• Clinical escalation pathways and diagnostic decision-support models
• Medical device validation, calibration, compliance, and patient safety standards
He is recognized for identifying subclinical biomarker shifts that predict cardiovascular disease, diabetes, fatty liver, kidney disease, autoimmune inflammation, neurodegeneration, and accelerated biological aging long before conventional diagnosis.
Role at IntelliNewz
At IntelliNewz, Dr. Siddiqui serves as Founder, Chief Medical Editor, and Lead Clinical Validator. Every article published is:
Evidence-based
• Clinically verified
• Technology-grounded
• Free from commercial bias
• Designed for real-world patient and physician decision-making
Through his writing, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health intelligence, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust — grounded in decades of frontline medical practice.
Contact:
powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content on IntelliNewz is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical consultation. For individual health concerns, please consult your physician.