Foods & Supplements to Boost Mood
This document explores the intricate relationship between diet, supplementation, and mood regulation. Foods & Supplements to Boost Mood delves into specific foods and supplements known for their potential mood-boosting properties, examining the underlying mechanisms through which they influence neurotransmitter production, reduce inflammation, and support overall brain health.
This guide aims to provide practical insights into incorporating these elements into your daily life to promote a more positive and balanced emotional state.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network linking the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. This connection plays a crucial role in mood regulation, as the gut microbiome influences neurotransmitter production, inflammation, and stress response.
Probiotics: These beneficial bacteria can improve gut health, which in turn can positively impact mood. Studies have shown that probiotics can reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. Good sources include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha.
Prebiotics: These are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, prebiotics can indirectly improve mood. Sources include garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, and oats.
Foods Rich in Mood-Boosting Nutrients
Certain foods contain nutrients that are essential for neurotransmitter synthesis and overall brain function, contributing to improved mood.
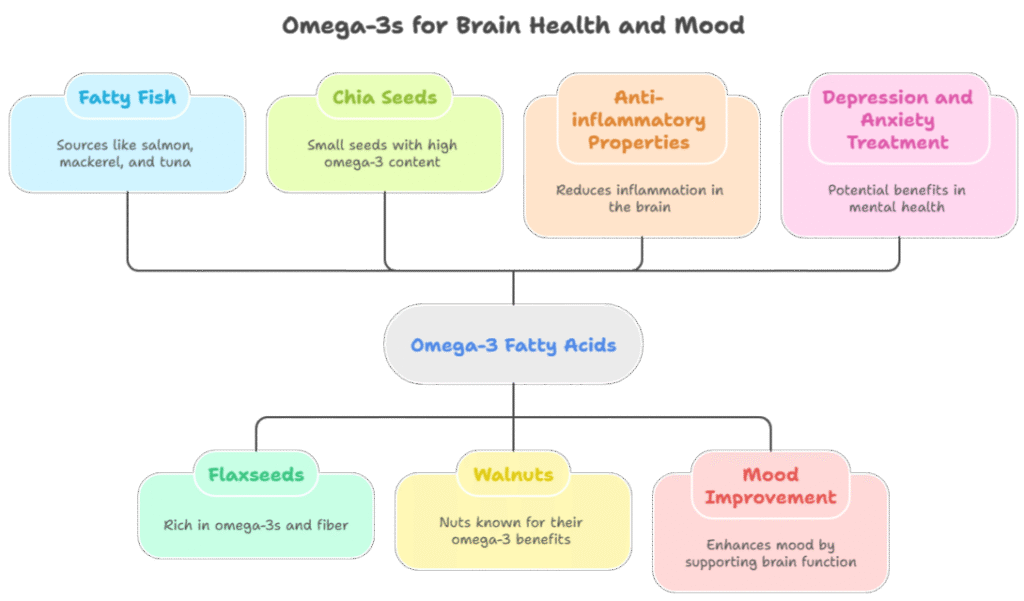
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for brain health. They have anti-inflammatory properties and can improve mood by supporting healthy brain cell function. Studies suggest that omega-3s can be beneficial in treating depression and anxiety.
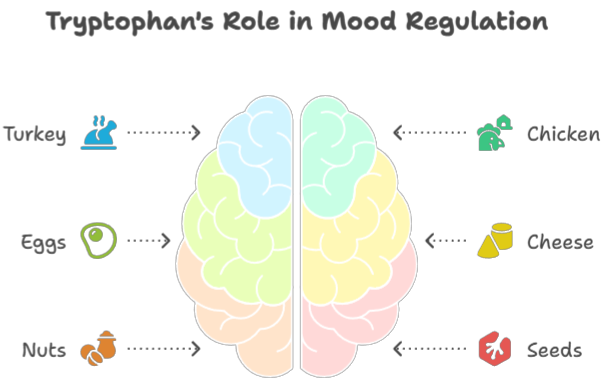
Tryptophan-Rich Foods: Tryptophan is an amino acid that the body uses to produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. Foods rich in tryptophan include turkey, chicken, eggs, cheese, nuts, and seeds.
Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to mood disorders, including depression. While sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, certain foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products can contribute to vitamin D intake.
Magnesium-Rich Foods: Magnesium is involved in numerous biochemical reactions in the body, including those related to mood regulation. Deficiency in magnesium can lead to anxiety, depression, and irritability. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), nuts, seeds, whole grains, and dark chocolate.
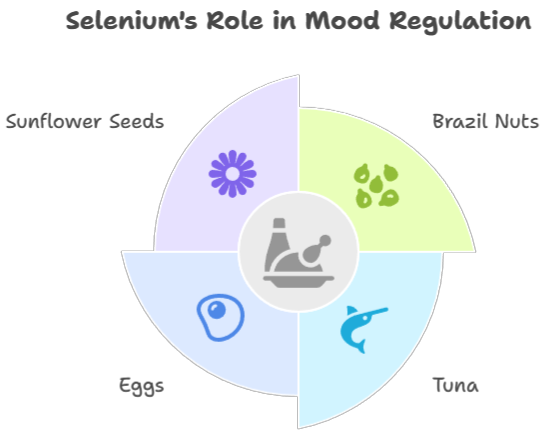
Selenium-Rich Foods: Selenium is an essential trace mineral that acts as an antioxidant and supports thyroid function, which is important for mood regulation. Foods rich in selenium include Brazil nuts, tuna, eggs, and sunflower seeds.
B Vitamins: B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for brain function and neurotransmitter synthesis. Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to mood disorders. Foods rich in B vitamins include whole grains, meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and legumes.
Supplements for Mood Enhancement
In addition to dietary changes, certain supplements can help boost mood by addressing nutrient deficiencies or supporting neurotransmitter function.
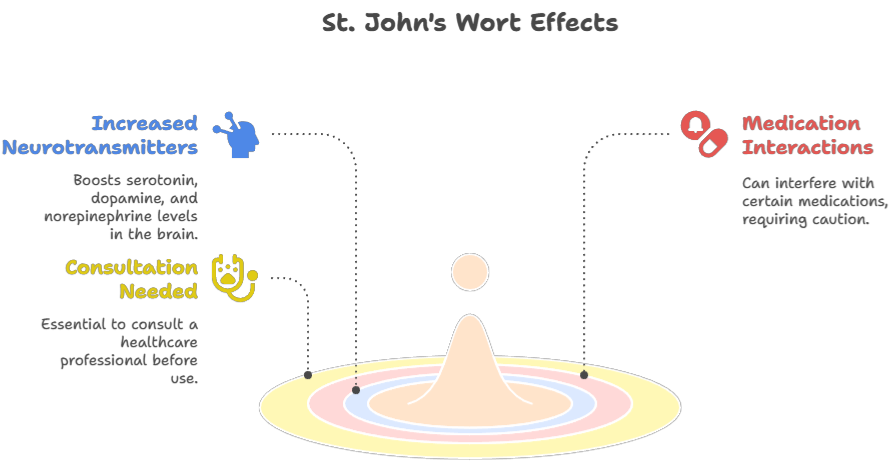
St. John’s Wort: This herbal supplement has been used for centuries to treat mild to moderate depression. It is believed to work by increasing the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain. However, St. John’s Wort can interact with certain medications, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using it.
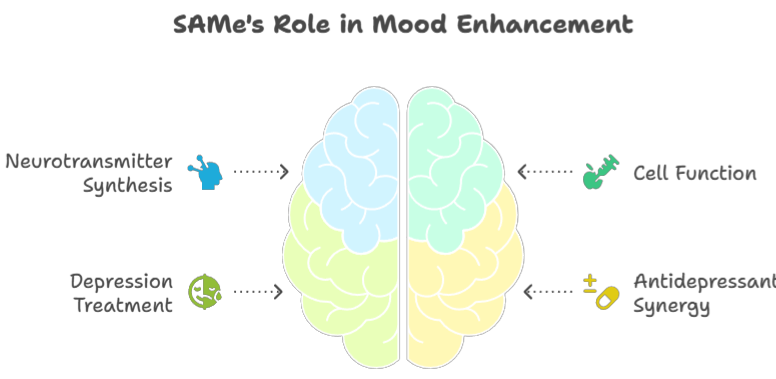
SAMe (S-Adenosylmethionine): SAMe is a naturally occurring compound in the body that plays a role in neurotransmitter synthesis and cell function. Studies have shown that SAMe can be effective in treating depression, particularly when used in conjunction with antidepressants.
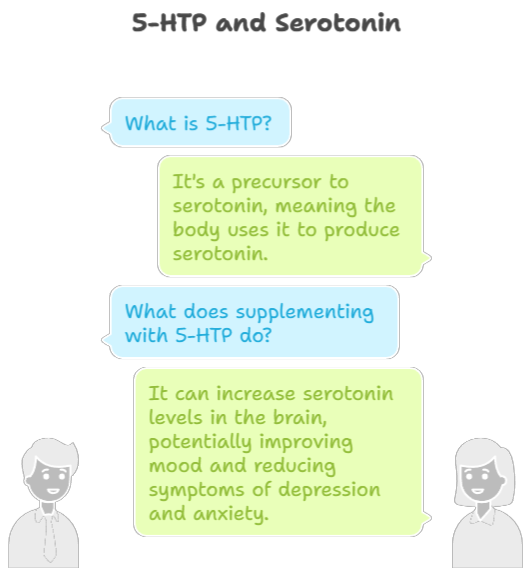
5-HTP (5-Hydroxytryptophan): 5-HTP is a precursor to serotonin, meaning the body uses it to produce serotonin. Supplementing with 5-HTP can increase serotonin levels in the brain, potentially improving mood and reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Vitamin D Supplements: If you have a vitamin D deficiency, supplementing with vitamin D can improve mood and overall well-being. It’s important to have your vitamin D levels checked by a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage.
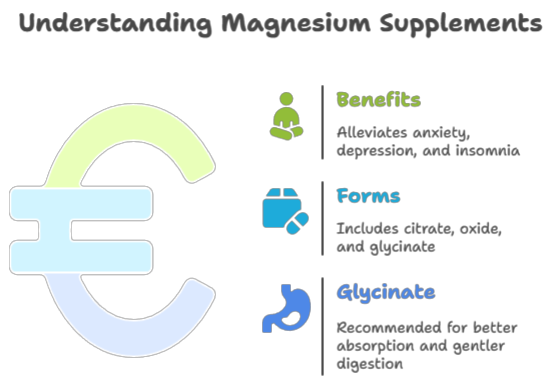
Magnesium Supplements: Magnesium supplements can be beneficial for individuals who are deficient in magnesium or who experience symptoms of anxiety, depression, or insomnia. Different forms of magnesium are available, such as magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide, and magnesium glycinate. Magnesium glycinate is often recommended for its better absorption and gentler effect on the digestive system.
Omega-3 Supplements: If you don’t consume enough fatty fish, supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids can help improve mood and brain health. Look for supplements that contain both EPA and DHA, the two primary types of omega-3 fatty acids.
Lifestyle Factors
While diet and supplementation play a significant role in mood regulation, other lifestyle factors are also important.
Regular Exercise: Exercise has been shown to improve mood by releasing endorphins, reducing stress, and improving sleep. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Sufficient Sleep: Sleep deprivation can negatively impact mood and cognitive function. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
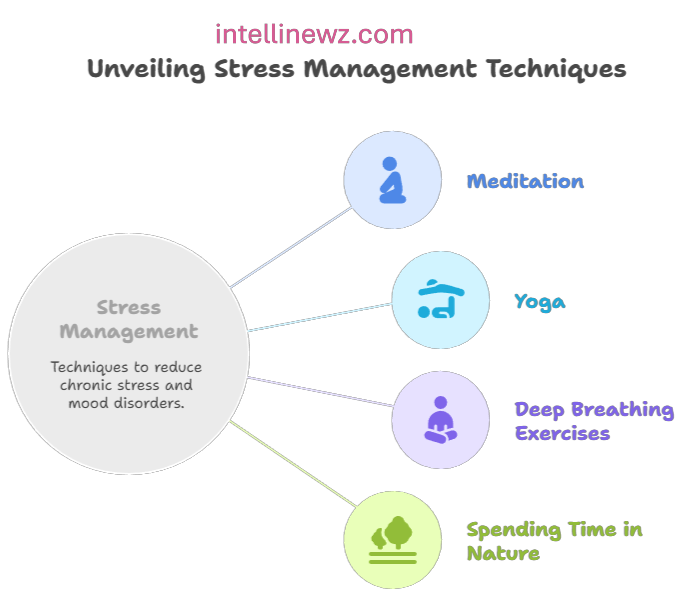
Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to mood disorders. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature.
Social Connection: Social isolation can lead to feelings of loneliness and depression. Make an effort to connect with friends and family, join social groups, or volunteer in your community.
Important Considerations
Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Before making significant changes to your diet or starting any new supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. They can help you determine the appropriate course of action based on your individual needs and health conditions.
Medication Interactions: Certain supplements can interact with medications, so it’s crucial to inform your doctor about any supplements you are taking.
Individual Variability: The effects of foods and supplements on mood can vary from person to person. What works for one individual may not work for another.
Holistic Approach: Diet and supplementation are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to mood regulation. It’s important to adopt a holistic approach that includes lifestyle factors such as exercise, sleep, stress management, and social connection.
By incorporating these foods, supplements, and lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can support your brain health and promote a more positive and balanced emotional state. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your individual needs.
What Is Nutritional Psychiatry?
Nutritional psychiatry explores how food influences brain chemistry, mood, and mental health. A nutrient-dense Mediterranean-style diet has been shown to reduce depression and anxiety, proving that food truly is medicine.
Key Nutrients for a Healthy Mind
| Nutrient | Why It Matters | Food Sources | Recommended Supplement* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduce inflammation & aid neurotransmission | Salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts | Triple-Strength Fish Oil |
| B Vitamins (B6, B12, Folate) | Support serotonin & dopamine | Leafy greens, legumes | Methyl B-Complex |
| Magnesium | Calms stress hormones & aids sleep | Pumpkin seeds, almonds | Magnesium Glycinate |
| Zinc | Supports neurotransmitter balance | Chickpeas, dark chocolate | Zinc Picolinate |
| Probiotics | Improve gut-brain communication | Yogurt, kefir, kimchi | High-Potency Probiotic |
*Always consult your healthcare provider before starting new supplements.
Mind–Gut Connection
Your gut microbiome—often called the “second brain”—sends chemical signals to the central nervous system. Fermented foods and prebiotic fibers help reduce inflammation and support a stable mood.
Lifestyle Pairings for Mental Wellness
Nutrition works best when combined with other healthy habits:
- Regular movement—even brisk walking improves brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports cognitive health.
- Consistent sleep to regulate hormones and stress response.
- Mindfulness or stress-reduction practices like meditation or yoga.
Key Takeaway
Food is more than fuel—it’s a powerful tool for mental health. By choosing nutrient-dense meals and supporting gut health, you can help protect your brain, stabilize mood, and reduce the risk of anxiety and depression.
Shop the Brain-Boosting Collection
Find all these supplements and more in our Amazon Nutritional Psychiatry Collection—each purchase supports your wellness journey.
Disclaimer: Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS
Registered Medical Practitioner (Reg. No. 39739)
With over 30 years of dedicated clinical experience, Dr. Siddiqui has built his career around one clear mission: making quality healthcare affordable, preventive, and accessible.
He is deeply passionate about:
- Early disease diagnosis – empowering patients with timely detection and reducing complications.
- Preventive healthcare – guiding individuals and families towards healthier, longer lives through lifestyle interventions and screenings.
- Affordable treatments – ensuring cost-effective, evidence-based medical solutions that reach people from all walks of life.
Through his blog, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health insights, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust. Every article is rooted in evidence-based medicine and enriched by decades of hands-on clinical practice.
Contact us on: powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not replace personalized medical consultation. For specific health concerns, please consult your physician. **********This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thanks for supporting the blog!***************************************************************
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS, M.Tech (Biomedical Engineering – VIT, Vellore)
Registered Medical Practitioner – Reg. No. 39739
Physician • Clinical Engineer • Preventive Diagnostics Specialist
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui is a physician–engineer with over 30 years of dedicated clinical and biomedical engineering experience, committed to transforming modern healthcare from late-stage disease treatment to early detection, preventive intelligence, and affordable medical care.
He holds an MBBS degree in Medicine and an M.Tech in Biomedical Engineering from VIT University, Vellore, equipping him with rare dual expertise in clinical medicine, laboratory diagnostics, and medical device engineering. This allows him to translate complex laboratory data into precise, actionable preventive strategies.
Clinical Mission
Dr. Siddiqui’s professional mission centers on three core pillars:
Early Disease Detection
Identifying hidden biomarker abnormalities that signal chronic disease years before symptoms appear — reducing complications, hospitalizations, and long-term disability.
Preventive Healthcare
Guiding individuals and families toward longer, healthier lives through structured screenings, lifestyle intervention frameworks, and predictive diagnostic interpretation.
Affordable Evidence-Based Treatment
Delivering cost-effective, scientifically validated care accessible to people from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
Clinical & Technical Expertise
Across three decades of continuous practice, Dr. Siddiqui has worked extensively with:
Advanced laboratory analyzers and automation platforms
• Cardiac, metabolic, renal, hepatic, endocrine, and inflammatory biomarker systems
• Preventive screening and early organ damage detection frameworks
• Clinical escalation pathways and diagnostic decision-support models
• Medical device validation, calibration, compliance, and patient safety standards
He is recognized for identifying subclinical biomarker shifts that predict cardiovascular disease, diabetes, fatty liver, kidney disease, autoimmune inflammation, neurodegeneration, and accelerated biological aging long before conventional diagnosis.
Role at IntelliNewz
At IntelliNewz, Dr. Siddiqui serves as Founder, Chief Medical Editor, and Lead Clinical Validator. Every article published is:
Evidence-based
• Clinically verified
• Technology-grounded
• Free from commercial bias
• Designed for real-world patient and physician decision-making
Through his writing, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health intelligence, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust — grounded in decades of frontline medical practice.
Contact:
powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content on IntelliNewz is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical consultation. For individual health concerns, please consult your physician.


