This document provides an overview of unwanted facial hair in women, exploring its causes, available treatment options, and management strategies. It aims to offer comprehensive information to individuals seeking to understand and address this common concern.
Understanding Unwanted Facial Hair
Unwanted facial hair, also known as hirsutism, refers to the excessive growth of dark or coarse hair in women in areas where hair growth is typically minimal or absent, such as the face, chest, and back. While some fine, light hair (vellus hair) is normal on a woman’s face, hirsutism involves the development of thicker, darker hair (terminal hair) in a male-like pattern.
Causes of Unwanted Facial Hair
Several factors can contribute to the development of unwanted facial hair in women:
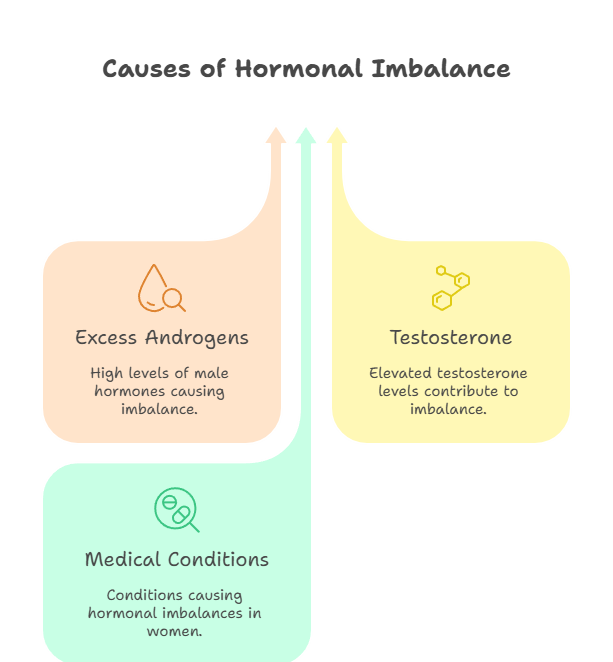
- Hormonal Imbalance: The most common cause is an imbalance of hormones, specifically an excess of androgens (male hormones) like testosterone. This imbalance can be caused by conditions such as:
* **Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):** PCOS is a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and elevated androgen levels. It is a leading cause of hirsutism.* **Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH):** This genetic condition affects the adrenal glands, leading to increased androgen production.* **Cushing's Syndrome:** This condition results from prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol, which can also increase androgen production.* **Ovarian Tumors or Adrenal Tumors:** In rare cases, tumors in the ovaries or adrenal glands can produce excess androgens, leading to hirsutism.- Medications: Certain medications can also cause hirsutism as a side effect, including:
* Anabolic steroids* Testosterone* Danazol* Glucocorticoids* Cyclosporine* Phenytoin- Genetics and Ethnicity: Family history and ethnicity can play a role in the likelihood of developing hirsutism. Women of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian descent are more prone to developing unwanted facial hair.
- Idiopathic Hirsutism: In some cases, the cause of hirsutism cannot be identified. This is known as idiopathic hirsutism. It is often thought to be due to increased sensitivity of hair follicles to normal levels of androgens.
Diagnosis
A doctor can diagnose hirsutism based on a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. They may also order blood tests to measure hormone levels, including testosterone, DHEAS, and other androgens. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans may be necessary to rule out ovarian or adrenal tumors.
Treatment Options
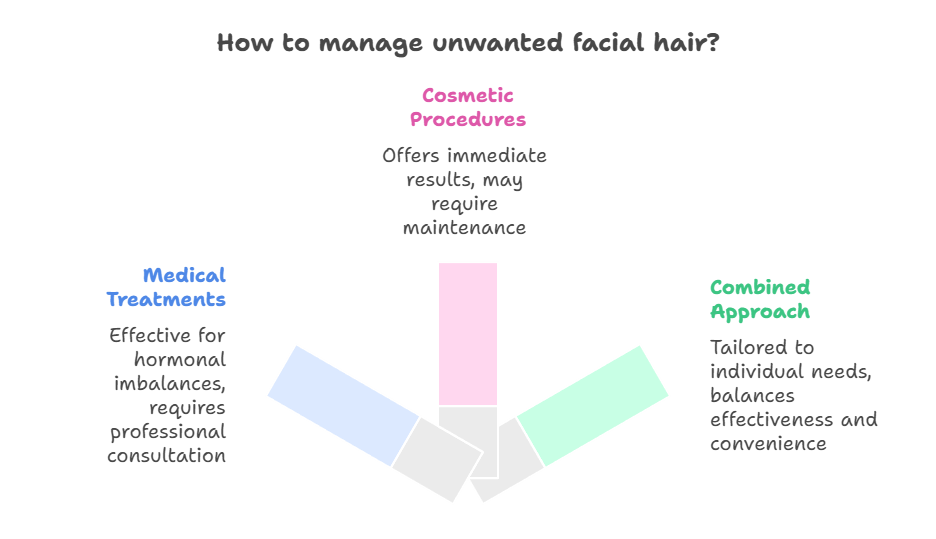
Treatment for unwanted facial hair typically involves a combination of medical and cosmetic approaches.
Cosmetic Treatments
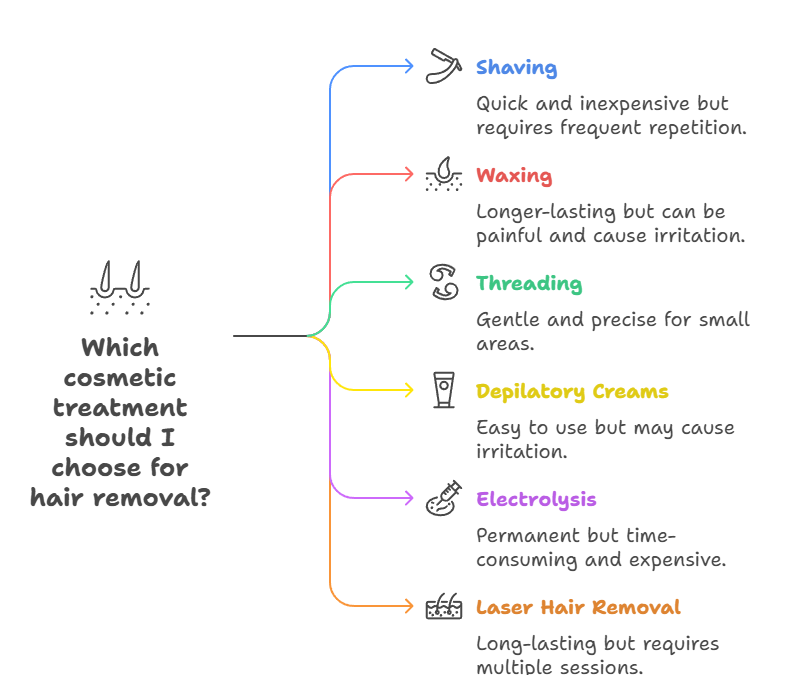
- Shaving: Shaving is a quick and inexpensive method of hair removal. However, it only removes hair at the surface and requires frequent repetition. It does not cause hair to grow back thicker or darker.
- Medical Treatments
- Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin can help regulate hormone levels and reduce androgen production. They are often the first-line treatment for hirsutism caused by PCOS.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: These medications block the effects of androgens on hair follicles. Common anti-androgens include:
* **Spironolactone:** This medication blocks androgen receptors and reduces androgen production.* **Cyproterone Acetate:** This medication is a potent anti-androgen that is often used in combination with estrogen.* **Flutamide:** This medication blocks androgen receptors but can have potential liver side effects.- Topical Cream: Eflornithine hydrochloride cream (Vaniqa) is a topical medication that can slow down hair growth. It does not remove existing hair but can reduce the rate of new hair growth.
Cosmetic Treatments
- Shaving: Shaving is a quick and inexpensive method of hair removal. However, it only removes hair at the surface and requires frequent repetition. It does not cause hair to grow back thicker or darker.
- Waxing: Waxing involves applying hot or cold wax to the skin and then quickly removing it, pulling out the hair from the root. It provides longer-lasting results than shaving but can be painful and cause skin irritation.
- Threading: Threading is an ancient hair removal technique that uses a twisted cotton thread to pluck hairs from the follicle. It is a gentle and precise method suitable for small areas like the eyebrows and upper lip.
- Depilatory Creams: These creams contain chemicals that dissolve hair at the surface of the skin. They are easy to use but can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions.
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis involves inserting a fine needle into each hair follicle and delivering an electric current to destroy the follicle. It is a permanent hair removal method but can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Laser Hair Removal: Laser hair removal uses concentrated beams of light to damage hair follicles, inhibiting hair growth. It is a long-lasting hair removal method but may require multiple sessions for optimal results. It is most effective on dark hair and light skin.
Management Strategies
In addition to medical and cosmetic treatments, several management strategies can help women cope with unwanted facial hair:
- Weight Management: For women with PCOS, weight loss can help improve hormone balance and reduce hirsutism.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and hormone balance.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
- Psychological Support: Unwanted facial hair can have a significant impact on a woman’s self-esteem and body image. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor can help address these emotional challenges.
Conclusion
Unwanted facial hair is a common concern for women, often caused by hormonal imbalances or genetic factors. Effective treatment options are available, ranging from medical interventions to cosmetic procedures. A combination of approaches, tailored to the individual’s specific needs and preferences, can help manage unwanted facial hair and improve quality of life. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
Through his blog, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health insights, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust. Every article is rooted in evidence-based medicine and enriched by decades of hands-on clinical practice.
Contact us on: powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not replace personalized medical consultation. For specific health concerns, please consult your physician.
**********This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thanks for supporting the blog!***************************************************************
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS, M.Tech (Biomedical Engineering – VIT, Vellore)
Registered Medical Practitioner – Reg. No. 39739
Physician • Clinical Engineer • Preventive Diagnostics Specialist
Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui is a physician–engineer with over 30 years of dedicated clinical and biomedical engineering experience, committed to transforming modern healthcare from late-stage disease treatment to early detection, preventive intelligence, and affordable medical care.
He holds an MBBS degree in Medicine and an M.Tech in Biomedical Engineering from VIT University, Vellore, equipping him with rare dual expertise in clinical medicine, laboratory diagnostics, and medical device engineering. This allows him to translate complex laboratory data into precise, actionable preventive strategies.
Clinical Mission
Dr. Siddiqui’s professional mission centers on three core pillars:
Early Disease Detection
Identifying hidden biomarker abnormalities that signal chronic disease years before symptoms appear — reducing complications, hospitalizations, and long-term disability.
Preventive Healthcare
Guiding individuals and families toward longer, healthier lives through structured screenings, lifestyle intervention frameworks, and predictive diagnostic interpretation.
Affordable Evidence-Based Treatment
Delivering cost-effective, scientifically validated care accessible to people from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
Clinical & Technical Expertise
Across three decades of continuous practice, Dr. Siddiqui has worked extensively with:
Advanced laboratory analyzers and automation platforms
• Cardiac, metabolic, renal, hepatic, endocrine, and inflammatory biomarker systems
• Preventive screening and early organ damage detection frameworks
• Clinical escalation pathways and diagnostic decision-support models
• Medical device validation, calibration, compliance, and patient safety standards
He is recognized for identifying subclinical biomarker shifts that predict cardiovascular disease, diabetes, fatty liver, kidney disease, autoimmune inflammation, neurodegeneration, and accelerated biological aging long before conventional diagnosis.
Role at IntelliNewz
At IntelliNewz, Dr. Siddiqui serves as Founder, Chief Medical Editor, and Lead Clinical Validator. Every article published is:
Evidence-based
• Clinically verified
• Technology-grounded
• Free from commercial bias
• Designed for real-world patient and physician decision-making
Through his writing, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health intelligence, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust — grounded in decades of frontline medical practice.
Contact:
powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content on IntelliNewz is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical consultation. For individual health concerns, please consult your physician.